Description
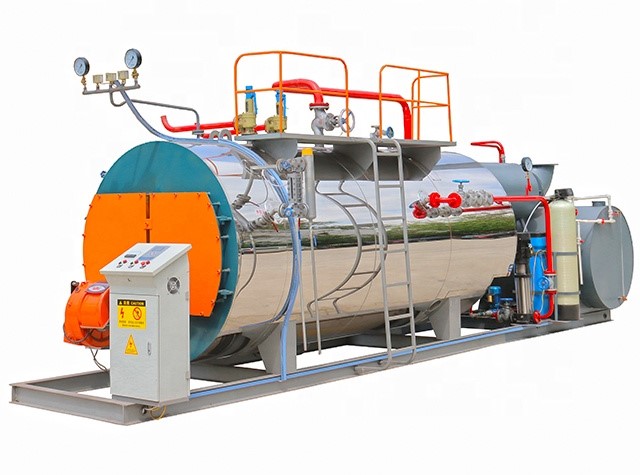
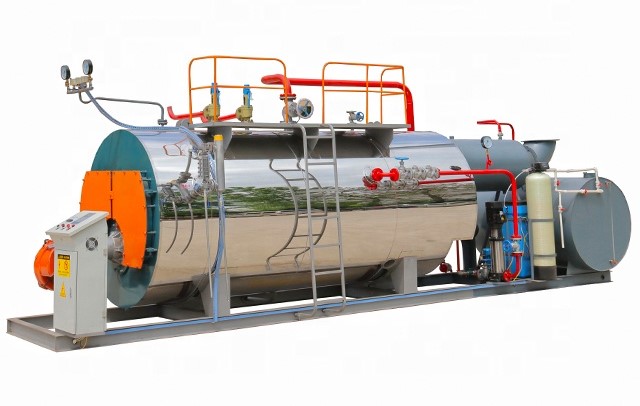
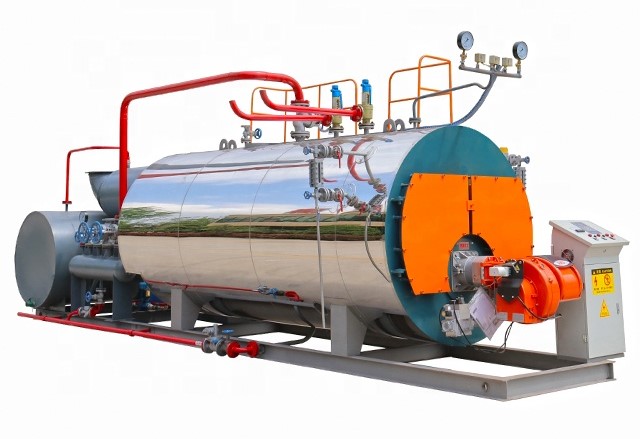
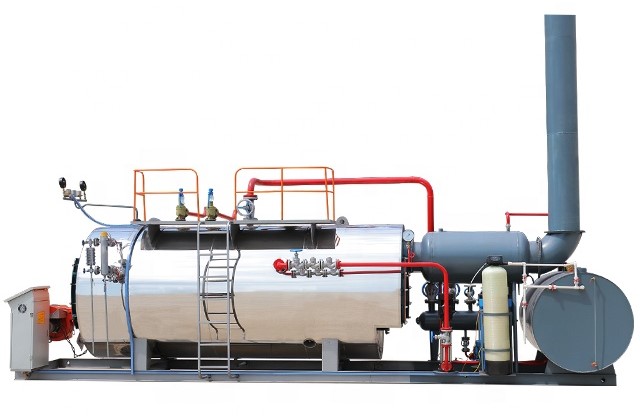
 Our boilers can burn any liquid or gaseous fuel; and come in sizes from 50 to 500 horsepower with pressures to 450 PSI. Our boilers are designed and engineered with larger furnaces, providing for inherently lower NOx emissions. To produce lower emissions, our boilers employ technologies such as; gas and air pre-mix, flue gas recirculation, and thermal reduction. We have also developed new control systems that utilize microprocessor-based fuel/air ratios offering superior combustion.
Our boilers can burn any liquid or gaseous fuel; and come in sizes from 50 to 500 horsepower with pressures to 450 PSI. Our boilers are designed and engineered with larger furnaces, providing for inherently lower NOx emissions. To produce lower emissions, our boilers employ technologies such as; gas and air pre-mix, flue gas recirculation, and thermal reduction. We have also developed new control systems that utilize microprocessor-based fuel/air ratios offering superior combustion.
Our Boilers are designed and engineered with larger furnaces. Also, these larger furnaces enable us to provide for inherently lower NOx emissions. In addition, new control systems offer superior combustion, utilizing microprocessor-based fuel/air ratio controls.
Finally, research and development projects are maintained in-house, as we continually strive to provide boiler solutions to meet all federal and state requirements, while greatly reducing “greenhouse” gasses.
Standard Features
Durability
Built in accordance with the ASME Code, the wet back design has proven to give much longer useful life cycles than dry back boilers.
Quality
Each unit is tested and inspected and registered with the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors.
Design
Our Boiler utilizes state of the art computer design techniques in every boiler. In addition, this accounts for accurate calculations of construction materials and optimum utilization of the boiler’s performance criteria.
Efficiency
Our boiler is designed for optimum fuel efficiency and has proven in certified tests to meet, and often exceed, the efficiencies of four-pass boilers.
Tube Sheets
The wet back has independent tube sheets with uniform temperatures. Additionally, three and four pass dry back boilers have tube sheets with large temperature variations and this results in premature tube failure and cracks in the tube sheets.
Easy Access
Since there is no large refractory rear door, one man can easily remove the rear cover plates for access to the tubes. In addition, front doors can be opened without removing burner components or controls.
Are you interested in other utilities?
Air Compressor / Dryer?
Chillers?
Installation
Installing a steam boiler requires careful planning and adherence to safety and regulatory standards. Here are comprehensive installation procedures:
Pre-Installation Preparation
Site Assessment:
- Choose a well-ventilated location with sufficient space for boiler installation, maintenance, and access to fuel sources.
- Ensure the flooring is level, capable of supporting the weight of the boiler, and resistant to moisture.
Permits and Regulations:
- Obtain necessary permits and approvals from local authorities and regulatory agencies.
- Ensure compliance with building codes, safety standards, and environmental regulations.
Utilities and Connections:
- Determine the fuel source (natural gas, oil, propane, etc.) and ensure adequate supply lines are in place.
- Plan for water supply and drainage connections, including condensate disposal.
Boiler Installation Steps
Foundation and Support:
- Install a solid foundation or base for the boiler, ensuring it is level and stable.
- Use appropriate materials, such as concrete or steel supports, to securely anchor the boiler.
Boiler Placement:
- Position the boiler on the foundation, aligning it with service connections and clearances as per manufacturer specifications.
- Allow sufficient space around the boiler for access to controls, valves, and maintenance points.
Piping and Connections:
- Connect water supply lines to the boiler inlet and ensure proper isolation valves are installed.
- Install blowdown and drain lines, including necessary traps and vents for safe operation.
Ventilation and Exhaust:
- Install ventilation ducts and flues to safely exhaust combustion gases.
- Ensure vents are directed away from occupied areas and comply with clearance requirements.
Electrical Wiring:
- Connect electrical wiring to the boiler controls, pumps, and safety devices.
- Ensure all wiring is grounded and protected according to electrical codes.
Safety Devices and Controls:
- Install safety valves, pressure gauges, temperature sensors, and control switches per manufacturer guidelines.
- Calibrate and test safety devices to ensure proper operation and compliance with safety standards.
Insulation and Sealing:
- Insulate steam pipes and boiler components to minimize heat loss and improve energy efficiency.
- Seal joints and connections to prevent leaks and maintain system integrity.
Commissioning and Testing:
- Fill the boiler with water and perform a hydrostatic test to check for leaks and verify system integrity.
- Purge air from the system and start up the boiler to test operational functions, including burner ignition and safety shutdowns.
Documentation and Training:
- Compile installation records, including equipment manuals, drawings, and test results.
- Provide training for boiler operators on system operation, maintenance procedures, and safety protocols.
Final Inspection and Certification:
- Conduct a final inspection to ensure all installation requirements are met and systems are functioning correctly.
- Obtain certification of compliance from regulatory authorities and arrange for periodic inspections as required.
Following these installation procedures ensures the steam boiler is installed safely, efficiently, and in accordance with industry standards and regulations. Proper installation is essential for reliable boiler performance, longevity, and operational safety.
Maintenance
Maintaining a steam boiler is crucial for ensuring safety, efficiency, and longevity. Here are essential maintenance procedures to follow:
- Regular Inspection:
- Conduct daily checks on boiler water level, pressure readings, and temperature.
- Inspect burner operation for proper ignition and flame stability.
- Check for leaks, unusual noises, or vibrations.
- Water Level Monitoring:
- Maintain proper water levels using gauge glass or electronic level controls.
- Ensure the feedwater supply is adequate and free from contaminants.
- Water Treatment:
- Implement a water treatment program to prevent scale buildup and corrosion.
- Test water quality regularly and adjust chemical dosing as needed.
- Blowdown Procedures:
- Conduct regular blowdown to remove sediments and impurities from the boiler.
- Follow recommended intervals based on water quality and boiler usage.
- Safety Valve Testing:
- Test safety valves periodically to ensure they open at the correct pressure.
- Verify the valve discharge path is clear and free from obstructions.
- Combustion Efficiency:
- Monitor burner efficiency and adjust air-to-fuel ratios for optimal combustion.
- Clean burner components and inspect for wear or carbon deposits.
- Inspection of Controls and Instruments:
- Check and calibrate pressure gauges, temperature sensors, and control switches.
- Verify operation of safety interlocks and alarms.
- Boiler Shell and Tubes:
- Inspect boiler internals for signs of corrosion, erosion, or leakage.
- Clean tubes and remove scale buildup using appropriate methods.
- Electrical System Maintenance:
- Inspect wiring, connections, and electrical components for wear or damage.
- Ensure safety devices, such as limit switches and flame detectors, are operational.
- Record Keeping:
- Maintain a logbook of maintenance activities, inspections, and test results.
- Document any repairs, adjustments, or incidents for historical reference.
- Training and Personnel Safety:
- Ensure boiler operators are trained in safety procedures and operational protocols.
- Provide personal protective equipment (PPE) and maintain a safe working environment.
- Emergency Preparedness:
- Develop and review emergency procedures for boiler shutdown, evacuation, and response to incidents.
- Conduct regular drills to ensure personnel are familiar with emergency protocols.
Following these maintenance procedures helps ensure the steam boiler operates safely, efficiently, and complies with regulatory standards. Regular inspections and proactive maintenance reduce downtime, extend equipment life, and minimize operational costs.
 Our boilers can burn any liquid or gaseous fuel; and come in sizes from 50 to 500 horsepower with pressures to 450 PSI. Our boilers are designed and engineered with larger furnaces, providing for inherently lower NOx emissions. To produce lower emissions, our boilers employ technologies such as; gas and air pre-mix, flue gas recirculation, and thermal reduction. We have also developed new control systems that utilize microprocessor-based fuel/air ratios offering superior combustion.
Our boilers can burn any liquid or gaseous fuel; and come in sizes from 50 to 500 horsepower with pressures to 450 PSI. Our boilers are designed and engineered with larger furnaces, providing for inherently lower NOx emissions. To produce lower emissions, our boilers employ technologies such as; gas and air pre-mix, flue gas recirculation, and thermal reduction. We have also developed new control systems that utilize microprocessor-based fuel/air ratios offering superior combustion.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.